摘 要
数控机床即数字程序控制机床,是一种自动化机床,数控技术是数控机床研究的核心,是制造业实现自动化、网络化、柔性化、集成化的基础。随着制造技术的发展,现代数控机床借助现代设计技术、工序集约化和新的功能部件使机床的加工范围、动态性能、加工精度和可靠性有了极大的提高。
本文主要对XK5040数控立式铣床及控制系统进行设计,首先分析立式铣床的加工特点和加工要求确定其主参数,包括运动和动力参数;根据主参数和设计要求进行主运动系统、进给系统和控制系统硬件电路设计。主要进行主运动系统和进给系统的机械结构设计及滚珠丝杠和步进电机的选型和校核;对于控制系统由于这里主要针对经济型数控铣床的设计,这里采用步进电机开环控制,计算机系统采用高性能价格比的MCS-51系列单片扩展系统,主要进行中央处理单元的选择、存储器扩展和接口电路设计。
由于本文采用8031单片机控制系统,因此,设计出的立式铣床性能价格比高,满足经济性要求。可实用于加工精度较高的场合。
关键词 数控技术;立式铣床;设计
ABSTRACT
The numerical control engine bed is the digital process control engine bed, is one kind of automated engine bed, the numerical control technology is the core which the numerical control engine bed studies, is the manufacturing industry realization automation, the network, the flexibility, the integrated foundation. Along with the manufacture technology development, the modern numerical control engine bed with the aid of the modern design technology, the working procedure intensification and the new function part caused the engine bed the processing scope, the dynamic performance, the processing precision and the reliability had the enormous enhancement .
This article mainly carries on the design to the XK5040 numerical control vertical milling machine and the control system, first analyzes the vertical milling machine the processing characteristic and the processing request determines its host parameter, including movement and dynamic parameter; Carry on the host kinematic scheme according to the host parameter and the design request, enters for the system and the control system hardware circuit design. Mainly carries on the host kinematic scheme and enters for the system mechanism design and the ball bearing guide screw and electric stepping motor shaping and the examination; Regarding control system because here mainly aims at the economy numerical control milling machine the design, here uses electric stepping motor open-loop control, the computer system uses the high performance price compared to the MCS-51 series monolithic expansion system, mainly carries on the central processing element the choice, the memory expansion and the connection circuit design .
Because this article uses 8,031 monolithic integrated circuits control system, therefore, designs the vertical milling machine performance price is higher than, satisfies the efficient request. But practical to processing precision higher situation .
Key words Numerical control technology; Vertical milling machine; Design
铣床是一种用途广泛的机床。它可以加工平面(水平面、垂直面等)、沟槽(键槽、T型槽、燕尾槽等)、多齿零件上齿槽(齿轮、链轮、棘轮、花键轴等)、螺旋形表面(螺纹和螺旋槽)及各种曲面。此外,它还可以用于加工回转体表面及内孔,以及进行切断工作等。
由于铣床使用旋转的多齿刀具加工工件,同时有数个刀齿参加切削,所以生产效率高,但是,由于铣刀每个刀齿的切削过程是断续的,且每一个的切削厚度又是变化的,这就使切削力相应地发生变化,容易引起机床振动,因此,铣床在结构上要求有较高的刚度和抗振性。
铣床的类型很多,主要类型有:卧式升降台铣床、立式升降台铣床、龙门铣床、工具铣床和各种专门化铣床等。
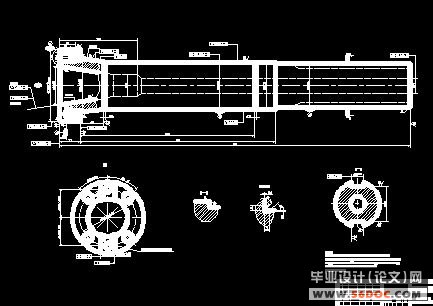
随着科学技术的进步,数控铣床得到了越来越广泛的应用,它一般分为立式和卧式两种,一般数控铣床是指规格较小的升降台数控铣床,其工作台宽度多在400mm以下,规格较大的数控铣床,例如工作台宽度在500mm以上的,其功能已向加工中心靠近,进而演变成柔性制造单元。数控铣床多为三坐标、两轴联动的机床,也称两轴半控制,即X、Y、Z三个坐标轴中,任意两个都可以联动。一般情况下,在数控铣床上只能用来加工平面曲线的轮廓。对于有特殊要求的数控铣床,还可以加进一个回转的A坐标或C坐标,即增加一个数控分度头或数控回转工作台,这是机床的数控系统为四坐``标的数控系统,它可用来加工旋转槽、叶片等立体曲面零件。
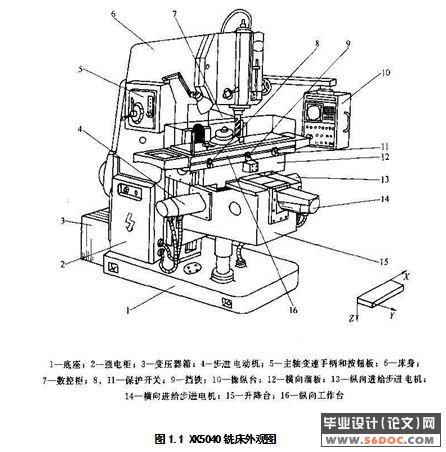
我们本次设计过程中要接触到的为XK5040数控立式铣床。它的工作台宽度为400mm。
目 录 35000字
摘 要 1
1 总体设计 5
1.1、铣床简介 5
1.2、 XK5040型数控铣床的总体布局、主要技术参数及总传动系统图 5
1.2.1 XK5040型数控铣床的总体布局 5
1.2.2 XK5040型数控铣床的主要技术参数 6
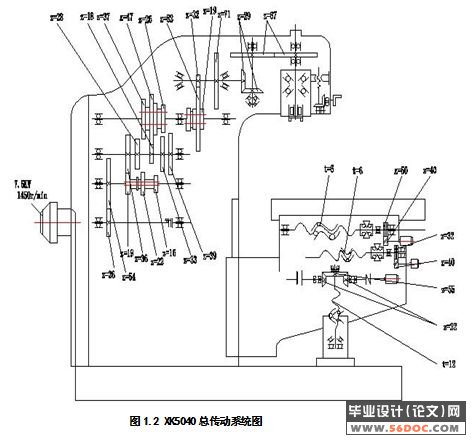
1.2.3 总传动系统图 8
2 主运动系统设计 9
2.1 传动系统设计 9
2.1.1参数的拟定 9
2.1.2 传动结构或结构网的选择 9
2.1.3 转速图拟定 11
2.1.4齿轮齿数的确定及传动系统图的绘制 13
2.2 传动件的估算与验算 16
2.2.1传动轴的估算和验算 16
2.2.2齿轮模数的估算 19
2.3 展开图设计 24
2.3.1结构实际的内容及技术要求 24
2.3.2 齿轮块的设计 25
2.3.3 传动轴设计 27
2.3.4 主轴组件设计 30
2.4 制动器设计 35
2.4.1 按扭矩选择 35
2.5 截面图设计 36
2.5.1 轴的空间布置 37
2.5.2 操纵机构 37
2.5.3 润滑 37
2.5.4箱体设计的确有关问题 38
3 进给系统设计 40
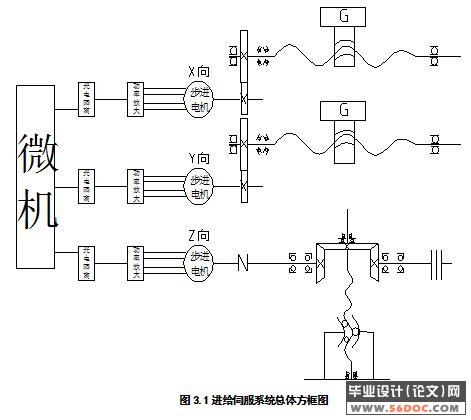
3.1 总体方案设计 40
3.1.1对进给伺服系统的基本要求 40
3.1.2进给伺服系统的设计要求 40
3.1.3总体方案 41
3.2 进给伺服系统机械部分设计 41
3.2.1确定脉冲当量,计算切削力 41
3.2.2滚珠丝杆螺母副的计算和造型 43
3.2.3齿轮传动比计算 52
3.2.4 步进电机的计算和选型 53
3.2.5 进给伺服系统机械部分结构设计 62
4 控制系统设计 66
4.1绘制控制系统结构框图 66
4.2.选择中央处理单元(CPU)的类型 66
4.3存储器扩展电路设计 67
4.3.1程序存储器的扩展 67
4.3.2 数据存储器的扩展 68
4.4 I/O接口电路及辅助电路设计 68
4.4.1 I/O接口电路设计 68
4.4.2 步进电机接口及驱动电路 69
4.2.3 其他辅助电路 70
参考文献 73
致谢 74
附 录 75
参考文献
[1]、李福生主编,数控机床技术手册[M].北京:出版社,1996.1
[2]、曹金榜易锡麟,机床主轴变速箱设计指导[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1987.5
[3]、王爱玲、白恩远、赵学良、赵建国主编,现代数控机床[M].北京:国防工业出版社,2003.4
[4]、《机械设计手册》编辑组编,机床设计手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1986.12
[5]、《机械设计手册》联合编写组编,机械设计手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社,1987.12
[6]、周明衡主编,离合器、制动器选用手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2005.5
[7]、华东纺织工学院 哈尔滨工业大学 天津大学 主编,机床设计图册[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,1981.5
[8]李广弟 朱月绣 王绣山主编,单片机基础[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社,2004.10
[9]黄鹤汀主编,金属切削机床设计[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1999.12
[10]赵大兴 李天宝主编,现代工程图学[M].武汉:武汉科学技术出版社,2002.8
[11]顾维邦主编,金属切削机床概论[M].北京:机械的工业出版社,1999.7
[12]张维纪编著,金属切削原理及刀具[M].杭州:浙江大学出版社,2003.7
[13]甘永立主编,几何量公差与检测[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2001.4
[14]张建钢 胡大泽主编,数控技术[M].武汉:华中科技大学出版社,2000.8
[15]朱张校主编,工程材料[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2003.6
[16]濮良贵 陈庚梅主编,机械设计教程[M].西安:西北工业大学出版社,2003.2
|











