芯轴托架(落料冲孔复合模和弯曲模)设计(文献综述,设计说明书13600字,CAD图11张)
摘 要
根据零件的设计尺寸要求、材料要求以及批量生产等要求,在分析好零件的工艺性之后,再制定工艺方案。再通过工艺计算来确定此模具的设计流程。模具加工工艺已经成为重要发展方向中的一项先进的制造工艺,如现在在汽车,航空等方面都是在广泛的应用。但是模具的制造成本也是直接影响到制件成本和企业的经济效益。该模具设计的材料厚度比较薄只有1.5mm,弯曲的高度也不是很高,可以二次弯曲成功。精度也不算很高,一般都是在IT11-14级之间。在弯曲成形没有达到我们所需要的工件时,可以再在后面加上二次弯曲这样一道工序来保证得到我们需要的模具。冲压成形技术早已经成为国内外比较成熟的一种金属成型加工工序,各种板料零件都是用该方法加工的。其的优点有:高效率、 轻重量、 精度好、成本低,而且还有自动化和机械化等优点。在本次设计中,主要考虑筒形零件的落料冲孔以及弯曲的成型工艺。最终将落料冲孔再弯曲作为本零件的主要成形工艺。
关键词:复合模 ;落料 ;冲孔 ;弯曲
ABSTRACT
According to parts of the design requirements of size, material requirements and production requirements, technology is good, after analyzing the parts, and then develop technology program. And then to determine the mold design process by process calculation. Mold processing technology has become an important development direction of advanced manufacturing processes, such as are now widely used in the automotive, aviation and so on. However, the manufacturing cost of the mold parts is also a direct impact on the cost and economic efficiency of enterprises. The mold design and material thickness is thin and only 1mm, drawing the height is not very high, you can bend the secondary success. Accuracy is not too high, generally between IT11-14 level. In deep drawing the work did not meet what we need, we can then followed by the shaping of such a process to ensure that we get the required mold. Stamping technology has already become more mature at home and abroad of a metal forming process, a variety of sheet metal parts are processed by this method. Its advantages are: high efficiency, light weight, good accuracy, low cost, but also the advantages of automation and mechanization. In this design, the main consideration blanking punching a cylindrical part and a curved molding process. Eventually blanking punching and then bending a part of the main forming process.
Keywords: composite mold ; blanking ; punching ; bending

目 录
1. 绪 论 1
2. 零件及工艺性分析 3
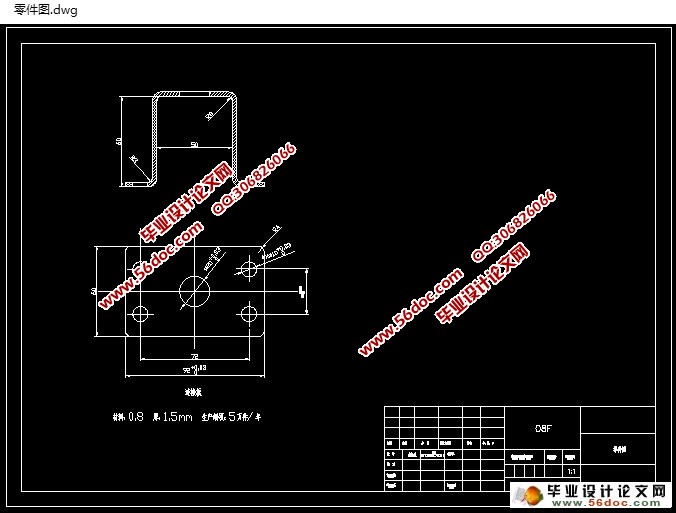
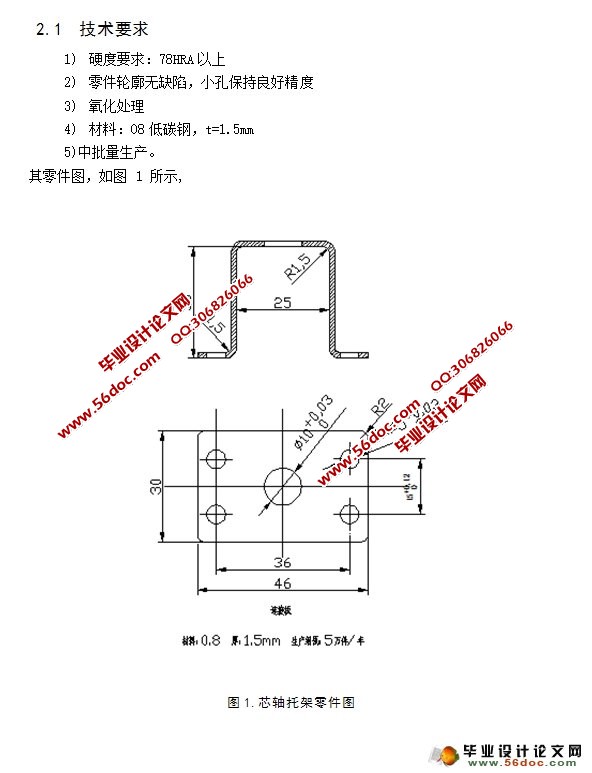
2.1 技术要求 3
2.2 读产品图,分析冲压工艺性 4
2.3 对零件的精度要求及分析 5
3. 分析计算确定工艺方案 6
3.1 主要工艺参数的计算 6
3.2 确定工艺方案 6
4. 一些重要的工艺参数的计算 12
4.1 确定排样、裁板方案 12
4.2 计算工艺力、选设备 13
4.2.1 落料力 13
4.2.2 卸料力 14
4.2.3 推件力 14
4.2.4 弯曲力(弯外角并使两内角预弯 ) 15
4.2.5 第二次弯曲(弯两内角) 15
4.2.6 冲裁力 16
4.2.7 卸料力 16
4.2.8 推件力 16
4.2.9 冲压设备选取 17
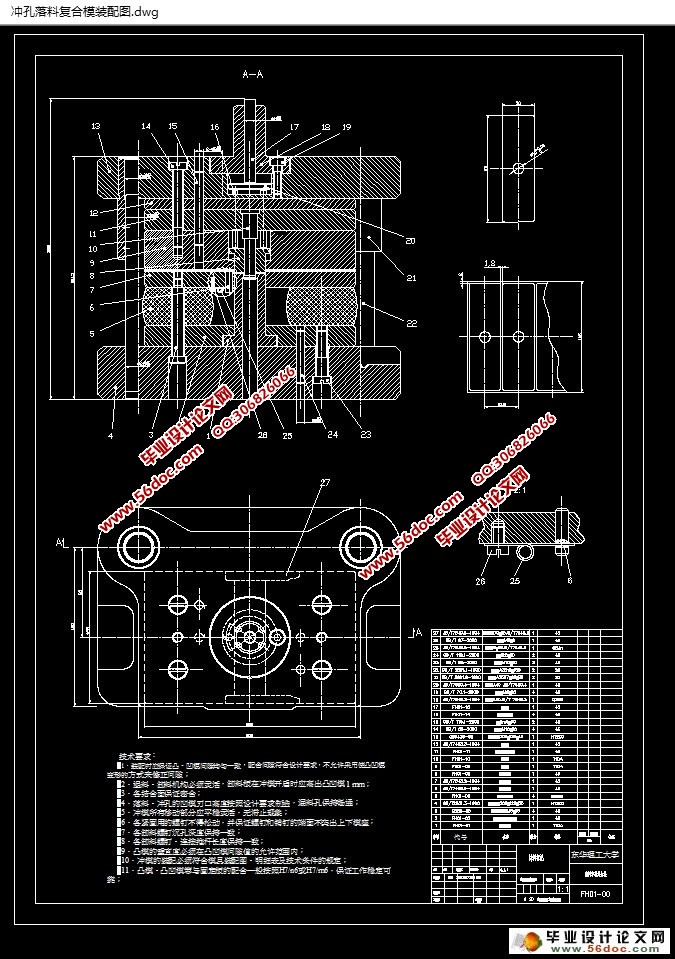
5 落料冲孔复合模的设计 18
5.1 模具结构设计 18
5.1.1 计算落料时的工作部位的刃口尺寸 18
5.1.2 计算冲孔时工作部件的尺寸 19
5.2 模具的工作零件尺寸的计算 20
5.2.1 落料凹模 20
5.2.2 冲孔凸模 20
5.2.3 凸凹模 22
5.3 模具的定位零件的设计 22
5.3.1 送料定距的确定 22
5.3.2 送进导向的确定 23
5.4 模具的卸料零件的确定 23
5.4.1 卸料板 23
5.4.2 卸料螺钉 23
5.4.3 橡胶的设计 23
5.5 推件装置的设计 24
5.5.1 推板 25
5.5.2 推件块的设计 26
5.5.3 连续推件及打杆的设计 26
5.6 选用模架、确定闭合高度及其它总体尺寸 27
5.6.1 凸模固定板的设计 27
5.6.2 垫板 28
5.6.3 螺钉与销钉的选择 28
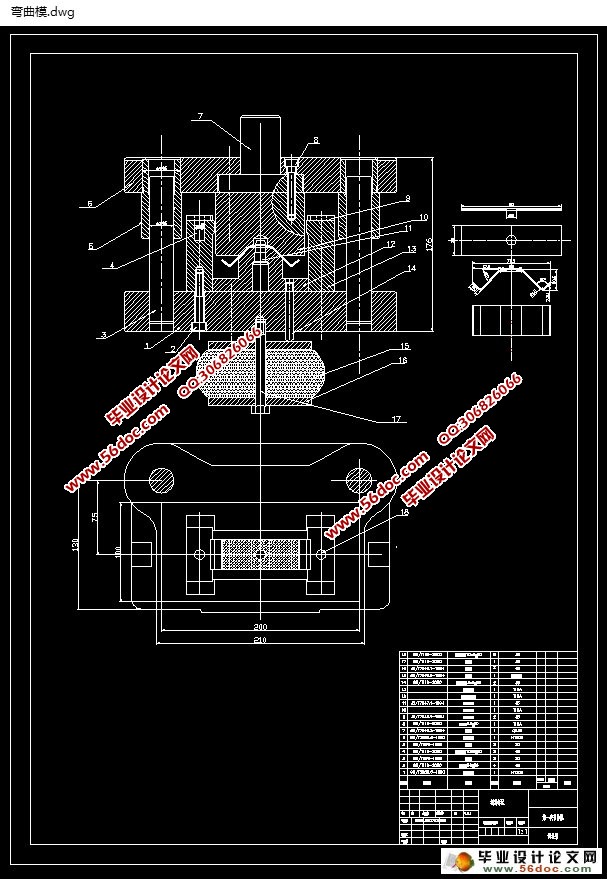
6 弯曲模具体设计 30
6.1 弯曲模工作部分尺寸的设计 30
6.1.1 弯曲凸模的圆角半径的确定 30
6.1.2 弯曲凹模的圆角半径确定 31
6.1.3 弯曲模的凹模深度的确定 31
6.1.4 凸、凹模间隙的设计 32
6.1.5 凸、凹模工作部分的尺寸与精度要求 33
6.1.6 弯曲凹凸模的设计 33
6.2 模具的定位零件的设计 34
6.2.1 导正销的设计 34
6.2.2 定位块的设计 34
6.2.3 推件装置的设计 34
6.2.5 垫板 35
7 冲孔模的设计 37
7.1 冲孔模尺寸计算 37
7.2 模具的工作零件尺寸的计算 37
7.2.1 冲孔凹模 37
7.2.2 冲孔凸模 38
7.3.1 导正销的设计 39
7.3.2 模具的卸料零件的确定 40
7.4 选模架、闭合高度和其它的尺寸计算 41
7.5 凸、凹模固定板的设计 42
7.6 垫板 42
7.7 螺钉与销钉 42
结 论 43
致 谢 44
参考文献 45
|











