封装件液态成形过程数值模拟与模具优化设计
来源:wenku163.com 资料编号:WK1633536 资料等级:★★★★★ %E8%B5%84%E6%96%99%E7%BC%96%E5%8F%B7%EF%BC%9AWK1633536
资料介绍
摘 要
随着铸造CAD/CAE实用化技术的发展及相应的商品化软件的应用,将这些先进的技术运用于产品的开发和质量的改进有着重要的经济和学术意义。本文结合工艺设计,数值模拟来完成模具的改进和优化。
本文通过对封装件液态成型的工艺特点的分析,用UG软件对上模、下模、砂芯进行了三维建模,利用Procast软件对铸件充型凝固过程进行了数值模拟。准确的反映了铸件充型凝固过程中的实际情况。通过对铸造过程中流场和温度场的分析,与预期成形效果做对比并以此针对模具进行优化设计。
关键词:CAD/CAE,铸件,铸造工艺,充型凝固过程,计算机模拟
ABSTRACT
As cast CAD/CAE practical technology get application progressively and the corresponding commercialized software is used in practice step by step,applying these advanced technology of CAD/CAE to product development and quality improving has very important economic and academic meanings.In this paper,die completion of the improvement and optimization combining the technical design numerical simulation .
In this paper,by the analysis to the characteristics of the packing of liquid molding process ,it utilizes design software Unigraphics NX to creat three-dimensional modeling for upper die and lower die and core,uses the numerical simulation software Procast to carry on filling and solidification numerical simulation analysis of casting .reflects actual state of castings accurately,predicts defect that may appers during filling and solidificating process then ascertains the position of the defect。through analyse the folw field and temerature fields and compared with the aimed forming effect to die completion the optimum design of the mould。
Key words: Computer Aided Design/Computer Aided Engineering,Casting,Casting technology,Filling and Solidification process,Copputer simulation

目 录 14000字
1 绪论 1
1.1 数字化产品开发国内外现状 1
1.1.1 计算机辅助设计软件 1
1.1.2 UG软件简介 1
1.1.3 ProCAST软件简介 2
1.1.4 MSC-Patran软件简介 6
1.1.5 封装的简介及其发展 7
1.1.6 离心铸造简介 8
1.2 课题学术和实用意义 9
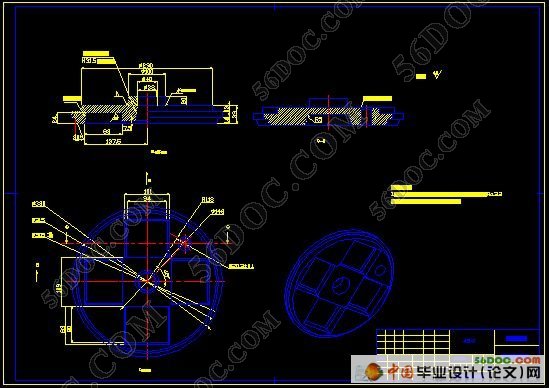
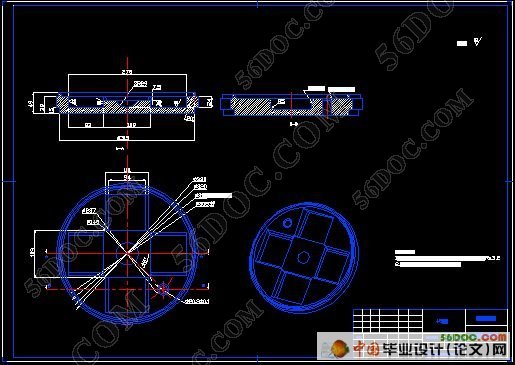
2 成形模具设计 11
2.1 零件结构分析 11
2.2 零件成形方法确定 11
2.3 浇注位置和分型面的确定 11
2.4 型芯设计 11
2.5 铸造工艺参数的确定 11
2.6 铸件在模具的布置 12
2.7 浇注系统设计 12
2.8 成形模具型腔结构设计 13
2.9 成形模具型腔外部结构设计 14
2.10 模具装配 15
3 数值模拟及结果分析 17
3.1 利用MSC-Patran划分网格 17
3.1.1 导入文件 17
3.1.2 划分网格 17
3.1.3 导出 17
3.2 装配网格图形 18
3.2.1 文件处理 18
3.2.2 装配网格图形 19
3.3 模拟的初始条件设置 19
3.3.1 检查网格 19
3.3.2 定义材料 20
3.3.3 定义界面的传热系数 21
3.3.4 定义边界条件 21
3.3.5 定义初始条件 22
3.3.6 定义运行参数 23
3.4 模拟过程及模拟结果的分析 23
3.4.1 模拟过程 23
3.4.2 模拟结果分析 23
结 论 29
参考文献 30
致 谢 31
附 录 32
|







